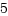name_to_handle_atシステムコール
Rev.1を表示中。最新版はこちら。
dfd/flagsでuser_path_at()でnameのpathを取得し、do_sys_name_to_handle()をコールしてfhandle/mount idを取得します。
SYSCALL_DEFINE5(name_to_handle_at, int, dfd, const char __user *, name,
struct file_handle __user *, handle, int __user *, mnt_id,
int, flag)
{
struct path path;
int lookup_flags;
int err;
if ((flag & ~(AT_SYMLINK_FOLLOW | AT_EMPTY_PATH)) != 0)
return -EINVAL;
lookup_flags = (flag & AT_SYMLINK_FOLLOW) ? LOOKUP_FOLLOW : 0;
if (flag & AT_EMPTY_PATH)
lookup_flags |= LOOKUP_EMPTY;
err = user_path_at(dfd, name, lookup_flags, &path);
if (!err) {
err = do_sys_name_to_handle(&path, handle, mnt_id);
path_put(&path);
}
return err;
}
ファイルのスーパブロックのコールバック関数s_export_op->fh_to_dentryが定義されなければエラーです。この関数はハンドルからdentryを取得するもので、これは実デバイスの読み書きを行うもので、ファイルシステムに直接依存します。(デフォルト処理が実装できない。)この処理がないとhandleを取得しても意味がありません。ufh->handle_bytesに応じたメモリを割り当て、exportfs_encode_fh()でufh->f_handleに(struct fid *)として、ファイル情報を設定します。返り値はhandleのタイプです。
static long do_sys_name_to_handle(struct path *path,
struct file_handle __user *ufh,
int __user *mnt_id)
{
long retval;
struct file_handle f_handle;
int handle_dwords, handle_bytes;
struct file_handle *handle = NULL;
if (!path->dentry->d_sb->s_export_op ||
!path->dentry->d_sb->s_export_op->fh_to_dentry)
return -EOPNOTSUPP;
if (copy_from_user(&f_handle, ufh, sizeof(struct file_handle)))
return -EFAULT;
if (f_handle.handle_bytes > MAX_HANDLE_SZ)
return -EINVAL;
handle = kmalloc(sizeof(struct file_handle) + f_handle.handle_bytes,
GFP_KERNEL);
if (!handle)
return -ENOMEM;
handle_dwords = f_handle.handle_bytes >> 2;
retval = exportfs_encode_fh(path->dentry,
(struct fid *)handle->f_handle,
&handle_dwords, 0);
handle->handle_type = retval;
handle_bytes = handle_dwords * sizeof(u32);
handle->handle_bytes = handle_bytes;
if ((handle->handle_bytes > f_handle.handle_bytes) ||
(retval == 255) || (retval == -ENOSPC)) {
handle_bytes = 0;
retval = -EOVERFLOW;
} else
retval = 0;
if (copy_to_user(mnt_id, &real_mount(path->mnt)->mnt_id,
sizeof(*mnt_id)) ||
copy_to_user(ufh, handle,
sizeof(struct file_handle) + handle_bytes))
retval = -EFAULT;
kfree(handle);
return retval;
}
ファイルシステムに応じたコールバック関数がコールされます。もし定義されていないとexport_encode_fh()がコールされます。
int exportfs_encode_fh(struct dentry *dentry, struct fid *fid, int *max_len,
int connectable)
{
const struct export_operations *nop = dentry->d_sb->s_export_op;
int error;
if (nop->encode_fh)
error = nop->encode_fh(dentry, fid->raw, max_len, connectable);
else
error = export_encode_fh(dentry, fid, max_len, connectable);
return error;
}
export_encode_fh()は32ビット長のinode番号で管理されるファイルシステムに適応され、ext2/3/4等が該当します。デフォルトでFILEID_INO32_GENでinode_no/inode_generationが設定され、システムコールから呼ばれた場合個のケースに当てはまります。カーネルサポートnfsのhandle取得で、引数のconnectableが0でなく、通常ファイルならその親のディレクトリのinode_no/inode_generationも設定され、FILEID_INO32_GEN_PARENTとなります。ファイル名の変更/削除/移動等の処理を実装するに、親のディレクトリ情報が必要となるからです。
static int export_encode_fh(struct dentry *dentry, struct fid *fid,
int *max_len, int connectable)
{
struct inode * inode = dentry->d_inode;
int len = *max_len;
int type = FILEID_INO32_GEN;
if (connectable && (len < 4)) {
*max_len = 4;
return 255;
} else if (len < 2) {
*max_len = 2;
return 255;
}
len = 2;
fid->i32.ino = inode->i_ino;
fid->i32.gen = inode->i_generation;
if (connectable && !S_ISDIR(inode->i_mode)) {
struct inode *parent;
spin_lock(&dentry->d_lock);
parent = dentry->d_parent->d_inode;
fid->i32.parent_ino = parent->i_ino;
fid->i32.parent_gen = parent->i_generation;
spin_unlock(&dentry->d_lock);
len = 4;
type = FILEID_INO32_GEN_PARENT;
}
*max_len = len;
return type;
}
ちなみに、handleタイプです。
enum fid_type {
/*
* The root, or export point, of the filesystem.
* (Never actually passed down to the filesystem.
*/
FILEID_ROOT = 0,
/*
* 32bit inode number, 32 bit generation number.
*/
FILEID_INO32_GEN = 1,
/*
* 32bit inode number, 32 bit generation number,
* 32 bit parent directory inode number.
*/
FILEID_INO32_GEN_PARENT = 2,
/*
* 64 bit object ID, 64 bit root object ID,
* 32 bit generation number.
*/
FILEID_BTRFS_WITHOUT_PARENT = 0x4d,
/*
* 64 bit object ID, 64 bit root object ID,
* 32 bit generation number,
* 64 bit parent object ID, 32 bit parent generation.
*/
FILEID_BTRFS_WITH_PARENT = 0x4e,
/*
* 64 bit object ID, 64 bit root object ID,
* 32 bit generation number,
* 64 bit parent object ID, 32 bit parent generation,
* 64 bit parent root object ID.
*/
FILEID_BTRFS_WITH_PARENT_ROOT = 0x4f,
/*
* 32 bit block number, 16 bit partition reference,
* 16 bit unused, 32 bit generation number.
*/
FILEID_UDF_WITHOUT_PARENT = 0x51,
/*
* 32 bit block number, 16 bit partition reference,
* 16 bit unused, 32 bit generation number,
* 32 bit parent block number, 32 bit parent generation number
*/
FILEID_UDF_WITH_PARENT = 0x52,
/*
* 64 bit checkpoint number, 64 bit inode number,
* 32 bit generation number.
*/
FILEID_NILFS_WITHOUT_PARENT = 0x61,
/*
* 64 bit checkpoint number, 64 bit inode number,
* 32 bit generation number, 32 bit parent generation.
* 64 bit parent inode number.
*/
FILEID_NILFS_WITH_PARENT = 0x62,
};
struct fid {
union {
struct {
u32 ino;
u32 gen;
u32 parent_ino;
u32 parent_gen;
} i32;
struct {
u32 block;
u16 partref;
u16 parent_partref;
u32 generation;
u32 parent_block;
u32 parent_generation;
} udf;
__u32 raw[0];
};
};
補足
inode_generationにinodeをアロケートする度に、インクリメントないしget_seconds()でxtimeの秒を設定したりしています。inode_noはファイルシステム下での管理で、ファイルシステムに関係なくinodeをリスト管理するために、inode_generationもキー情報とするために利用されているようです。とにかくこの2つの情報で、確実にファイルが特定できるということです。