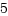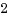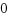ファイルディスクリプタ
Rev.2を表示中。最新版はこちら。
C言語でファイルを扱うときはFILEをもちいた、fopen・fread・fwrite・fclose などのライブラリ関数を使いますが、内部的にはopen・read・write・close などの、低レベルなシステムコールを利用しています。この時ファイルディスクリプタと呼ばれる整数値を使います。この整数値はtasku_struct->files_struct->fdable->fileの配列インデックということです。
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/sched.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/proc_fs.h>
#include <asm/uaccess.h>
#include <linux/fdtable.h>
#define PROC_NAME "hogehoge"
static size_t proc_write( struct file *filp, const char __user *buff,
unsigned long len, void *data );
static struct proc_dir_entry *dirp;
static int proc_init_module(void)
{
dirp = (struct proc_dir_entry *)
create_proc_entry(PROC_NAME, 0666, (struct proc_dir_entry *) 0);
if (dirp == 0)
return(-EINVAL);
dirp->write_proc = (write_proc_t *) proc_write;
return 0;
}
static void proc_cleanup_module(void)
{
remove_proc_entry(PROC_NAME, (struct proc_dir_entry *) 0);
}
static void do_file_struct(struct task_struct *process)
{
int open,i;
struct files_struct *files;
files = process->files;
int cnt = files->fdt->max_fds;
for (i = 0; i < cnt; i++) {
if (files->fdt->fd[i]) {
printk("fileid:%d filename:%s inode:%d\n",
i,
files->fdt->fd[i]->f_path.dentry->d_name.name,
files->fdt->fd[i]->f_path.dentry->d_inode->i_ino);
}
}
}
static size_t proc_write( struct file *filp, const char __user *buff,
unsigned long len, void *data )
{
char _buff[64];
if (copy_from_user(_buff, buff, len )) {
return -EFAULT;
}
int mypid = simple_strtol(_buff, NULL, 0);
struct task_struct *process;
process = find_task_by_vpid(mypid);
if (process) {
do_file_struct(process);
}
else {
mypid = -1;
printk("pid error:%d\n", mypid);
return -EFAULT;
}
return len;
}
module_init(proc_init_module);
module_exit(proc_cleanup_module);
確認プログラム
#include <stdio.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
main()
{
int fd1, fd2, fd3;
fd1 = open("a1", O_WRONLY | O_APPEND | O_CREAT);
fd2 = open("a2", O_WRONLY | O_APPEND | O_CREAT);
fd3 = open("a3", O_WRONLY | O_APPEND | O_CREAT);
printf("%d,%d,%d\n", fd1, fd2, fd3);
while(1) {
sleep(100);
}
}
[root@localhost test]# ./a.out & [1] 6738 [root@localhost test]# 3,4,5 [root@localhost test]# echo 6738 > /proc/hogehoge [root@localhost test]# dmesg fileid:0 filename:0 inode:2 fileid:1 filename:0 inode:2 fileid:2 filename:0 inode:2 fileid:3 filename:a1 inode:103376 fileid:4 filename:a2 inode:103379 fileid:5 filename:a3 inode:103381fileid:0,1,2はそれぞれ標準入力、標準出力、標準エラーです。iノードが同じです。ってことはその1つのiノードのオペレーションで入力、出力、エラーと処理しているのかな?