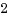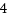open_by_handle_atシステムコール
name_to_handle_atで取得したfile_handleとmount idで、open_by_handle_atでファイルを参照します。運用はサーバで提供するファイルのfile_handleとmount idをクライアントに送信し、クライアントはそのファイル参照時、file_handleとmount idをサーバに返信する事で、サーバはパスに依存しないでファイル参照します。
open_by_handle_atの第一引数は、mount idでなく、そのファイルシステム下のファイルIDで、そのファイルをopenする事で、掛かるファイルシステムがunmountされていない事、そしてファイル参照中にそのファイルシステムがumontされないようにするためです。掛かるファイルシステムの任意のファイルが1つでもオープンされていれば、unmountできません。なお、AT_FDCWDとすると、カレントプロセスのカレントディレクトリのファイルシステムとなります。通常は/proc/self/mountinfoのmount idのマウントディレクトリをopenします。
サンプル
exportfs_decode_fh()で、取得したstruct vfsmountから、struct file_handleのinode_noのinodeを取得し、vfs_dentry_acceptableコールバックでそのinodeのdentryを取得します。
file_handle.f_handle[]をstruct fidとし、ファイルシステムに依存した管理情報が設定されます。
inode取得毎にinode->i_generationはインクリメントされ、inode番号が同じでもfid->i32.gen != inode->i_generationなら、そのファイルはオリジナルなファイルでなく、削除後新規に作成されたファイルとなり参照できません。
open_by_handle_atの第一引数は、mount idでなく、そのファイルシステム下のファイルIDで、そのファイルをopenする事で、掛かるファイルシステムがunmountされていない事、そしてファイル参照中にそのファイルシステムがumontされないようにするためです。掛かるファイルシステムの任意のファイルが1つでもオープンされていれば、unmountできません。なお、AT_FDCWDとすると、カレントプロセスのカレントディレクトリのファイルシステムとなります。通常は/proc/self/mountinfoのmount idのマウントディレクトリをopenします。
サンプル
#define _GNU_SOURCE
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#define errExit(msg) do { perror(msg); exit(EXIT_FAILURE); \
} while (0)
void main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
struct file_handle *fhp;
int mount_id, mount_fd, fd, nread;
char buf[128], *mount_fd_file;
fhp = malloc(sizeof(struct file_handle) + MAX_HANDLE_SZ);
if (fhp == NULL){
errExit("malloc");
}
fhp->handle_bytes = MAX_HANDLE_SZ;
if (name_to_handle_at(AT_FDCWD, "/mnt4/babakaka1", fhp, &mount_id, 0) == -1){
errExit("name_to_handle_at");
}
mount_fd_file = (argc == 2)? argv[1]: "/mnt4";
printf("%s\n", mount_fd_file);
mount_fd = open(mount_fd_file, O_RDONLY);
if (mount_fd == -1)
errExit("open_fd");
printf("%d\n", mount_fd);
fd = open_by_handle_at(mount_fd, fhp, O_RDONLY);
if (fd == -1)
errExit("open_by_handle_at");
memset(buf, 0, sizeof(buf));
nread = read(fd, buf, sizeof(buf));
close(fd);
if (nread == -1)
errExit("read");
printf("%s\n", buf);
}
[root@localhost north]# echo "abcdefg" > /mnt4/babakaka1
[root@localhost north]# touch /mnt4/babakaka2
[root@localhost north]# cat /proc/self/mountinfo | grep /mnt4
46 22 7:0 / /mnt4 rw,relatime - ext2 /dev/loop0 rw,user_xattr,acl,barrier=1
[root@localhost north]# ./a.out /mnt4/babakaka2
/mnt4/babakaka2
46
abcdefg
[root@localhost north]# ./a.out /mnt4
/mnt4
46
abcdefg
[root@localhost test]# ./a.out /
/
46
open_by_handle_at: Stale NFS file handle
get_vfsmount_from_fd()でmountdirfdのstruct file *fileからfile->f_path.mntでstruct vfsmountを取得します。AT_FDCWDならcurrent->fs->pwd.mntが取得されます。exportfs_decode_fh()で、取得したstruct vfsmountから、struct file_handleのinode_noのinodeを取得し、vfs_dentry_acceptableコールバックでそのinodeのdentryを取得します。
file_handle.f_handle[]をstruct fidとし、ファイルシステムに依存した管理情報が設定されます。
struct file_handle {
__u32 handle_bytes;
int handle_type;
/* file identifier */
unsigned char f_handle[0];
};
struct fid {
union {
struct {
u32 ino;
u32 gen;
u32 parent_ino;
u32 parent_gen;
} i32;
struct {
u32 block;
u16 partref;
u16 parent_partref;
u32 generation;
u32 parent_block;
u32 parent_generation;
} udf;
__u32 raw[0];
};
};
exportfs_decode_fh()でpath->mntからhandle->f_handleのinode番号からinodeを取得後そのdentryを取得します。
static int do_handle_to_path(int mountdirfd, struct file_handle *handle,
struct path *path)
{
int retval = 0;
int handle_dwords;
path->mnt = get_vfsmount_from_fd(mountdirfd);
if (IS_ERR(path->mnt)) {
retval = PTR_ERR(path->mnt);
goto out_err;
}
handle_dwords = handle->handle_bytes >> 2;
path->dentry = exportfs_decode_fh(path->mnt,
(struct fid *)handle->f_handle,
handle_dwords, handle->handle_type,
vfs_dentry_acceptable, NULL);
if (IS_ERR(path->dentry)) {
retval = PTR_ERR(path->dentry);
goto out_mnt;
}
return 0;
out_mnt:
mntput(path->mnt);
out_err:
return retval;
}
static struct vfsmount *get_vfsmount_from_fd(int fd)
{
struct path path;
if (fd == AT_FDCWD) {
struct fs_struct *fs = current->fs;
spin_lock(&fs->lock);
path = fs->pwd;
mntget(path.mnt);
spin_unlock(&fs->lock);
} else {
int fput_needed;
struct file *file = fget_light(fd, &fput_needed);
if (!file)
return ERR_PTR(-EBADF);
path = file->f_path;
mntget(path.mnt);
fput_light(file, fput_needed);
}
return path.mnt;
}
struct dentry *exportfs_decode_fh(struct vfsmount *mnt, struct fid *fid,
int fh_len, int fileid_type,
int (*acceptable)(void *, struct dentry *), void *context)
{
const struct export_operations *nop = mnt->mnt_sb->s_export_op;
struct dentry *result, *alias;
char nbuf[NAME_MAX+1];
int err;
if (!nop || !nop->fh_to_dentry)
return ERR_PTR(-ESTALE);
result = nop->fh_to_dentry(mnt->mnt_sb, fid, fh_len, fileid_type);
if (!result)
result = ERR_PTR(-ESTALE);
if (IS_ERR(result))
return result;
if (S_ISDIR(result->d_inode->i_mode)) {
if (result->d_flags & DCACHE_DISCONNECTED) {
err = reconnect_path(mnt, result, nbuf);
if (err)
goto err_result;
}
if (!acceptable(context, result)) {
err = -EACCES;
goto err_result;
}
return result;
} else {
struct dentry *target_dir, *nresult;
alias = find_acceptable_alias(result, acceptable, context);
if (alias)
return alias;
err = -ESTALE;
if (!nop->fh_to_parent)
goto err_result;
target_dir = nop->fh_to_parent(mnt->mnt_sb, fid,
fh_len, fileid_type);
if (!target_dir)
goto err_result;
err = PTR_ERR(target_dir);
if (IS_ERR(target_dir))
goto err_result;
err = reconnect_path(mnt, target_dir, nbuf);
if (err) {
dput(target_dir);
goto err_result;
}
err = exportfs_get_name(mnt, target_dir, nbuf, result);
if (!err) {
mutex_lock(&target_dir->d_inode->i_mutex);
nresult = lookup_one_len(nbuf, target_dir,
strlen(nbuf));
mutex_unlock(&target_dir->d_inode->i_mutex);
if (!IS_ERR(nresult)) {
if (nresult->d_inode) {
dput(result);
result = nresult;
} else
dput(nresult);
}
}
dput(target_dir);
alias = find_acceptable_alias(result, acceptable, context);
if (!alias) {
err = -EACCES;
goto err_result;
}
return alias;
}
err_result:
dput(result);
return ERR_PTR(err);
}
ext3のmnt->mnt_sb->s_export_opの.fh_to_dentryはext3_fh_to_dentry()です。
static const struct export_operations ext3_export_ops = {
.fh_to_dentry = ext3_fh_to_dentry,
.fh_to_parent = ext3_fh_to_parent,
.get_parent = ext3_get_parent,
};
static struct dentry *ext3_fh_to_dentry(struct super_block *sb, struct fid *fid,
int fh_len, int fh_type)
{
return generic_fh_to_dentry(sb, fid, fh_len, fh_type,
ext3_nfs_get_inode);
}
static struct dentry *ext3_fh_to_parent(struct super_block *sb, struct fid *fid,
int fh_len, int fh_type)
{
return generic_fh_to_parent(sb, fid, fh_len, fh_type,
ext3_nfs_get_inode);
}
get_inode()はファイルシステム依存で、ext3ではext3_nfs_get_inode()です。このinodeのdentryをd_obtain_alias()で取得します。この時dentryがキャッシュにない場合、親denrty配下に新規にdentryを作成する事になります。この時のファイル名は""です。
struct dentry *generic_fh_to_dentry(struct super_block *sb, struct fid *fid,
int fh_len, int fh_type, struct inode *(*get_inode)
(struct super_block *sb, u64 ino, u32 gen))
{
struct inode *inode = NULL;
if (fh_len < 2)
return NULL;
switch (fh_type) {
case FILEID_INO32_GEN:
case FILEID_INO32_GEN_PARENT:
inode = get_inode(sb, fid->i32.ino, fid->i32.gen);
break;
}
return d_obtain_alias(inode);
}
inode取得毎にinode->i_generationはインクリメントされ、inode番号が同じでもfid->i32.gen != inode->i_generationなら、そのファイルはオリジナルなファイルでなく、削除後新規に作成されたファイルとなり参照できません。
static struct inode *ext3_nfs_get_inode(struct super_block *sb,
u64 ino, u32 generation)
{
struct inode *inode;
if (ino < EXT3_FIRST_INO(sb) && ino != EXT3_ROOT_INO)
return ERR_PTR(-ESTALE);
if (ino > le32_to_cpu(EXT3_SB(sb)->s_es->s_inodes_count))
return ERR_PTR(-ESTALE);
inode = ext3_iget(sb, ino);
if (IS_ERR(inode))
return ERR_CAST(inode);
if (generation && inode->i_generation != generation) {
iput(inode);
return ERR_PTR(-ESTALE);
}
return inode;
}