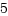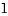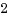list_splice(リスト結合)
list_splice()は、2つのlist_headリストを結合します。自明な事ですが、結合するリストは何らかのノードがある必要があります。
サンプルです。
static inline void list_splice(struct list_head *list, struct list_head *head)
{
if (!list_empty(list))
__list_splice(list, head);
}
static inline void __list_splice(struct list_head *list,
struct list_head *head)
{
struct list_head *first = list->next;
struct list_head *last = list->prev;
struct list_head *at = head->next;
first->prev = head;
head->next = first;
last->next = at;
at->prev = last;
}
頭の体操みたいな処理ですが、これは下記の様な処理となります。H2 | H1 6 4 | 3 1 5 | 2 結合前 結合後 4.prev=H2 -> 4.prev=H1 H1.next=1 -> H1.next=4 6.next=H2 -> 6.next=1 1.prev=H1 -> 1.prev=6結合されたH1リストは、H1->4->5->6->1->2->3->H1となります。なお、H2からリストだと、H2->4->5->6->1->2->3->H1->4 とH2に戻ってきませんので、もはやヘッドとしての意味を持っていません。
サンプルです。
[root@localhost lkm]# cat hogehoge.c
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/syscalls.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/moduleparam.h>
#include <linux/unistd.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/list.h>
#include <linux/slab.h>
static LIST_HEAD(head1);
static LIST_HEAD(head2);
struct my_object {
struct list_head list;
int sec;
};
void disp_obj(int sel);
int init_module(void)
{
struct my_object *myobj1, *myobj2;
struct list_head;
int i;
for (i = 1; i <= 5; ++i) {
myobj1 = (struct my_object *)kmalloc(sizeof(struct my_object), GFP_KERNEL);
myobj1->sec = i;
list_add_tail(&myobj1->list, &head1);
}
for (i = 6; i <= 10; ++i) {
myobj2 = (struct my_object *)kmalloc(sizeof(struct my_object), GFP_KERNEL);
myobj2->sec = i;
list_add_tail(&myobj2->list, &head2);
}
disp_obj(1);
list_splice(&head2, &head1);
disp_obj(0);
return 0;
}
void disp_obj(int sel)
{
struct list_head *p;
struct my_object *myobj;
char entry[256], tmp[6];
entry[0] = 0;
printk("list head 1\n");
list_for_each(p, &head1) {
myobj = list_entry(p, struct my_object, list);
sprintf(tmp, "%d->", myobj->sec);
strcat(entry, tmp);
}
strcat(entry, "\n");
printk(entry);
if (sel == 1) {
entry[0] = 0;
printk("list head 2\n");
list_for_each(p, &head2) {
myobj = list_entry(p, struct my_object, list);
sprintf(tmp, "%d->", myobj->sec);
strcat(entry, tmp);
}
strcat(entry, "\n");
printk(entry);
}
}
void cleanup_module(void)
{
struct my_object *myobj;
while(!list_empty(&head1)) {
myobj = list_entry(head1.next, struct my_object, list);
list_del(&myobj->list);
kfree(myobj);
}
}
[root@localhost lkm]# insmod hogehoge.ko [root@localhost lkm]# dmesg : : [ 340.101170] list head 1 [ 340.101170] 1->2->3->4->5-> [ 340.101170] list head 2 [ 340.101170] 6->7->8->9->10-> [ 340.101170] list head 1 [ 340.101170] 6->7->8->9->10->1->2->3->4->5->