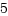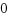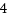fhandl
Linux man pages onlineの内容を実装を踏まえて書き改めて形となります。
ファイル読み書きは、そのファイルのパスをdentry走査し、そのdentryからのinodeのコールバック関数をfileオペレーションコールバックに設定し、ファイルの読み書きを行っています。fhandleはファイル名からファイル読み書きするのでなく、ファイルシステムのinode情報から直接ファイル読み書きするものです。
nfsではファイルパス等、各クライアント依存でリアルタイムに反映されません。実装によっては、クライアントサイドのキャッシュとも影響してきます。従ってファイルのやり取りは直接inodeで行った方が他のクライアントからの影響が少ないわけです。例えば、ファイルをrenameしてもinodeは同じです。従ってrenameに関係なく、rename前の名前で。というイメージでrenameされたファイルを読み書きできるわけです。ただし、inodeからファイルを取得すると言うことで、この実装はファイルシステム依存となります。なおファイルシステムにstruct export_operationsが設定されていなければ、サポートされません。
システムコールname_to_handle_atとopen_by_handle_atは、ユーザランドでnfsを実装するためのシステムコールらしく、下記サンプルは、Linux man pages onlineサンプルのエッセンスだけを抜き出し、見やすくしたものです。
fhandlesize_get()でstruct file_handle *fhpのサイズを取得しています。そこに設定されるinode情報はファイルシステムによって異なるからです。
fhandlesize_get()で/mntのファイルシステムのfhandleサイズを取得します。この時fh.handle_bytes = 0でname_to_handle_at()をコールすると、fhにはhandle_bytesとhandle_typeしか設定されません。取得したサイズメモリを確保したfphを取得し、fhandle_get()で/mnt/hogeのfhandlを取得します。
このfhandleでfhandle_read()をコールすることで、/mnt/hogeを読み出します。なお、/mnt/hogeのファイルシステムのマウントポイントのFILEIDが必要となります。実サンプルでは/proc/self/mountinfoからname_to_handle_at()で取得した/mnt/hogeのマウントIDからマウント先を取得するようになっていますが、ここでは/mntと決め打ちしています。一般ユーザはマウント先をunmountできません。従ってパス名を変更することもできません。
f_handle:1d:00:00:00=29で、 ls -iのi_noと一致します。
fhandlesize_get()でEOVERFLOWはエラーとしていません。
fhandleを取得するファイルと動作するプロセスのカレントディレクトリが、同じファイルシステムなら、
open_by_handle_at()でマウント先fileID引数を、マウント先fileIDでなくAT_FDCWDでコールする事ができます。
ファイル読み書きは、そのファイルのパスをdentry走査し、そのdentryからのinodeのコールバック関数をfileオペレーションコールバックに設定し、ファイルの読み書きを行っています。fhandleはファイル名からファイル読み書きするのでなく、ファイルシステムのinode情報から直接ファイル読み書きするものです。
nfsではファイルパス等、各クライアント依存でリアルタイムに反映されません。実装によっては、クライアントサイドのキャッシュとも影響してきます。従ってファイルのやり取りは直接inodeで行った方が他のクライアントからの影響が少ないわけです。例えば、ファイルをrenameしてもinodeは同じです。従ってrenameに関係なく、rename前の名前で。というイメージでrenameされたファイルを読み書きできるわけです。ただし、inodeからファイルを取得すると言うことで、この実装はファイルシステム依存となります。なおファイルシステムにstruct export_operationsが設定されていなければ、サポートされません。
システムコールname_to_handle_atとopen_by_handle_atは、ユーザランドでnfsを実装するためのシステムコールらしく、下記サンプルは、Linux man pages onlineサンプルのエッセンスだけを抜き出し、見やすくしたものです。
fhandlesize_get()でstruct file_handle *fhpのサイズを取得しています。そこに設定されるinode情報はファイルシステムによって異なるからです。
fhandlesize_get()で/mntのファイルシステムのfhandleサイズを取得します。この時fh.handle_bytes = 0でname_to_handle_at()をコールすると、fhにはhandle_bytesとhandle_typeしか設定されません。取得したサイズメモリを確保したfphを取得し、fhandle_get()で/mnt/hogeのfhandlを取得します。
このfhandleでfhandle_read()をコールすることで、/mnt/hogeを読み出します。なお、/mnt/hogeのファイルシステムのマウントポイントのFILEIDが必要となります。実サンプルでは/proc/self/mountinfoからname_to_handle_at()で取得した/mnt/hogeのマウントIDからマウント先を取得するようになっていますが、ここでは/mntと決め打ちしています。一般ユーザはマウント先をunmountできません。従ってパス名を変更することもできません。
#define _GNU_SOURCE
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <string.h>
void fhandle_read(int mount_fd, struct file_handle *fhp);
void fhandle_get(char* file, struct file_handle* fhp, int* mount_id);
int fhandlesize_get(char* path);
#define errExit(msg) do { perror(msg); exit(EXIT_FAILURE); \
} while (0)
int
main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
struct file_handle *fhp;
int mount_id, fhsize, flags, dirfd, j;
int size;
size = fhandlesize_get("/mnt/hoge");
fhsize = sizeof(struct file_handle) + size;
fhp = malloc(fhsize);
if (fhp == NULL)
errExit("realloc");
fhp->handle_bytes = size;
fhandle_get("/mnt/hoge", fhp, &mount_id);
fhandle_read(mount_id, fhp);
exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
}
int fhandlesize_get(char* path)
{
struct file_handle fh;
int mount_id;
fh.handle_bytes = 0;
if (name_to_handle_at(AT_FDCWD, path, &fh, &mount_id, 0) != -1 || errno != EOVERFLOW) {
fprintf(stderr, "Unexpected result from name_to_handle_at()\n");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
return fh.handle_bytes;
}
void fhandle_get(char* file, struct file_handle* fhp, int* mount_id)
{
int j;
if (name_to_handle_at(AT_FDCWD, "/mnt/hoge", fhp, mount_id, 0) == -1)
errExit("name_to_handle_at");
printf("mount :%d\n", *mount_id);
printf("size :%d\n", fhp->handle_bytes);
printf("type :%d\n", fhp->handle_type);
printf("f_handle:");
for (j = 0; j < fhp->handle_bytes; j++)
printf("%02x:", fhp->f_handle[j]);
printf("\n");
}
void fhandle_read(int mount_id, struct file_handle *fhp)
{
int fd, nread, mnt_fd;
char buf[64];
mnt_fd = open("/mnt", O_RDONLY);
if (fd == -1) {
printf("read pen err\n");
exit(1);
}
fd = open_by_handle_at(mnt_fd, fhp, O_RDONLY);
nread = read(fd, buf, sizeof(buf));
if (nread == -1)
errExit("read");
buf[nread] = 0;
printf("data :%s\n", buf);
}
[root@localhost kitamura]# echo abcdefg > /mnt/hoge
[root@localhost kitamura]# ./a.out
mount :43
size :8
type :1
f_handle:1d:00:00:00:86:75:c0:e3:
data :abcdefg
[root@localhost kitamura]# cat /proc/self/mountinfo | grep 43
43 22 8:17 / /mnt rw,relatime - ext3 /dev/sdb1 rw,user_xattr,acl,barrier=1,nodelalloc,data=ordered
handle_bytesはf_handleのバイトサイズ(インデックス数)、handle_typeはf_handle情報のタイプで、デフォルトはFILEID_INO32_GEN=1で、32ビット長さで、i_no/i_generationが設定されということです。f_handle:1d:00:00:00=29で、 ls -iのi_noと一致します。
struct file_handle {
__u32 handle_bytes;
int handle_type;
unsigned char f_handle[0];
};
[root@localhost kitamura]# ls -i /mnt/hoge
29 /mnt/hoge
補足
fh.handle_bytesが取得するファイルシステムのf_handle領域よりhandle_bytesが小さいとき、EOVERFLOWエラーとなり、そのメッセージがname_to_handle_at: Value too large for defined data typeとなります。fhandlesize_get()でEOVERFLOWはエラーとしていません。
fhandleを取得するファイルと動作するプロセスのカレントディレクトリが、同じファイルシステムなら、
open_by_handle_at()でマウント先fileID引数を、マウント先fileIDでなくAT_FDCWDでコールする事ができます。