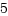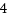PageCacheを覗いてみる
一度読み込んだファイルデータはページキャッシュとして、ページ単位でプロセスのfile->address_space->radix_tree_root->radix_tree_nodeに、radix-treeという形式で保存されています。そのページキャッシュを覗いてみたいと思います。
なお、キャッシュがページ(4012K)を満たない場合、radix-treeスロットが設定されるところに、直接ページキャッシュのアドレスが設定されるようになっているようです。検証はそれを前提にして行っています。
なお、キャッシュがページ(4012K)を満たない場合、radix-treeスロットが設定されるところに、直接ページキャッシュのアドレスが設定されるようになっているようです。検証はそれを前提にして行っています。
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/sched.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/proc_fs.h>
#include <asm/uaccess.h>
#include <linux/fdtable.h>
#include <linux/pagemap.h>
#define PROC_NAME "hogehoge"
static size_t proc_write( struct file *filp, const char __user *buff,
unsigned long len, void *data );
static struct proc_dir_entry *dirp;
static int proc_init_module(void)
{
dirp = (struct proc_dir_entry *)
create_proc_entry(PROC_NAME, 0666, (struct proc_dir_entry *) 0);
if (dirp == 0)
return(-EINVAL);
dirp->write_proc = (write_proc_t *) proc_write;
return 0;
}
static void proc_cleanup_module(void)
{
remove_proc_entry(PROC_NAME, (struct proc_dir_entry *) 0);
}
static void do_page_cache(struct task_struct *process)
{
int i, ans = 0;
struct files_struct *files;
struct address_space *mapping;
struct radix_tree_node *node;
struct page *page;
files = process->files;
// ファイルaのファイルディスクリプターの取得
for (i = 0; i < files->fdt->max_fds; i++) {
if (files->fdt->fd[i]) {
if (!strcmp(files->fdt->fd[i]->f_path.dentry->d_name.name, "a")) {
ans = 1;
break;
}
}
}
if (ans) {
mapping = files->fdt->fd[i]->f_mapping;
// 本来これがradix-treeスロットバッファーのポインターになるのですが、
// ページは1つだけということでここにページキャッシュのページが設定されるようです。
node = mapping->page_tree.rnode;
page = node;
// kmapはpageをリニアアドレスに変換するマクロです。
printk("%s\n", kmap(page));
}
return 0;
}
static size_t proc_write( struct file *filp, const char __user *buff,
unsigned long len, void *data )
{
char _buff[64];
if (copy_from_user(_buff, buff, len )) {
return -EFAULT;
}
int mypid = simple_strtol(_buff, NULL, 0);
struct task_struct *process;
process = find_task_by_vpid(mypid);
if (process) {
do_do_page_cache(process);
}
else {
mypid = -1;
printk("pid error:%d\n", mypid);
return -EFAULT;
}
return len;
}
module_init(proc_init_module);
module_exit(proc_cleanup_module);
ユーザプロセス
#include <stdio.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
main()
{
int fd;
char buff[100];
fd = open("a", O_RDONLY);
if (fd) {
read(fd, buff, sizeof(buff));
printf("%s\n", buff);
while(1)
sleep(100);
}
}
aファイルを作成してユーザプロセスを起動[root@localhost test]# echo "abcdefghijklmn" > a [root@localhost test]# ./a.out & [1] 5184 [root@localhost test]# abcdefghijklmn起動したユーザプロセスIDを/proc/hogehogeに書き込む
[root@localhost test]# ps PID TTY TIME CMD 1479 pts/0 00:00:03 bash 5184 pts/0 00:00:00 a.out 5185 pts/0 00:00:00 ps [root@localhost test]# echo 5184 > /proc/hogehoge [root@localhost test]# dmesg abcdefghijklmn