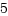コマンドのcap
コマンド実行は、do_execve()からprepare_binprm()を、そこでSEC linuxでないならcap_bprm_set_creds()でCAPが設定されます。
get_file_caps()では、まずcap_permitted/cap_inheritable/cap_effectiveがクリアされ、ファイルのxattrに設定してあるCAPが設定されます。通常未設定故、従って非rootならcap_permitted/cap_inheritable/cap_effective=0となります。
実ユーザ(uid)または、実効ユーザ(euid)がrootなら、new->cap_permitted=old->cap_bset | old->cap_inheritableとし、euidがrootの時のみ、new->cap_effective = new->cap_permittedとなります。
デフォルト実装では、cap_bset=~0で、従って、old->cap_inheritableに関係なくcap_permitted=~0となり、struct cred init_credの.cap_bset = CAP_FULL_SETを.cap_bset = CAP_EMPTY_SETとして構築すれば、cap_inheritable機能継承としての意味合いの実装ができます。
issecure(SECURE_NOROOT)は、rootプロセスであってもCAPを設定できないようにするためで、credのケーパビリティみたいなものです。current->cred->securebitsに設定してあり、他に SECURE_NO_SETUID_FIXUP(uid変更時、capabilityは更新しない。)SECURE_KEEP_CAPS(rootから非root変更時、CAPを更新しない。)があります。デフォルトではcurrent->cred->securebits=0で、全て無効でprctlシステムコールで設定できます。
・uid=0/ueid!=0のケース
・uid=0/ueid=0のケース
get_file_caps()では、まずcap_permitted/cap_inheritable/cap_effectiveがクリアされ、ファイルのxattrに設定してあるCAPが設定されます。通常未設定故、従って非rootならcap_permitted/cap_inheritable/cap_effective=0となります。
実ユーザ(uid)または、実効ユーザ(euid)がrootなら、new->cap_permitted=old->cap_bset | old->cap_inheritableとし、euidがrootの時のみ、new->cap_effective = new->cap_permittedとなります。
デフォルト実装では、cap_bset=~0で、従って、old->cap_inheritableに関係なくcap_permitted=~0となり、struct cred init_credの.cap_bset = CAP_FULL_SETを.cap_bset = CAP_EMPTY_SETとして構築すれば、cap_inheritable機能継承としての意味合いの実装ができます。
issecure(SECURE_NOROOT)は、rootプロセスであってもCAPを設定できないようにするためで、credのケーパビリティみたいなものです。current->cred->securebitsに設定してあり、他に SECURE_NO_SETUID_FIXUP(uid変更時、capabilityは更新しない。)SECURE_KEEP_CAPS(rootから非root変更時、CAPを更新しない。)があります。デフォルトではcurrent->cred->securebits=0で、全て無効でprctlシステムコールで設定できます。
int cap_bprm_set_creds(struct linux_binprm *bprm)
{
const struct cred *old = current_cred();
struct cred *new = bprm->cred;
bool effective, has_cap = false;
int ret;
effective = false;
ret = get_file_caps(bprm, &effective, &has_cap);
if (ret < 0)
return ret;
if (!issecure(SECURE_NOROOT)) {
if (has_cap && new->uid != 0 && new->euid == 0) {
warn_setuid_and_fcaps_mixed(bprm->filename);
goto skip;
}
if (new->euid == 0 || new->uid == 0) {
/* pP' = (cap_bset & ~0) | (pI & ~0) */
new->cap_permitted = cap_combine(old->cap_bset,
old->cap_inheritable);
}
if (new->euid == 0)
effective = true;
}
skip:
if (!cap_issubset(new->cap_permitted, old->cap_permitted))
bprm->per_clear |= PER_CLEAR_ON_SETID;
if ((new->euid != old->uid ||
new->egid != old->gid ||
!cap_issubset(new->cap_permitted, old->cap_permitted)) &&
bprm->unsafe & ~LSM_UNSAFE_PTRACE_CAP) {
/* downgrade; they get no more than they had, and maybe less */
if (!capable(CAP_SETUID)) {
new->euid = new->uid;
new->egid = new->gid;
}
new->cap_permitted = cap_intersect(new->cap_permitted,
old->cap_permitted);
}
new->suid = new->fsuid = new->euid;
new->sgid = new->fsgid = new->egid;
if (effective)
new->cap_effective = new->cap_permitted;
else
cap_clear(new->cap_effective);
bprm->cap_effective = effective;
if (!cap_isclear(new->cap_effective)) {
if (!cap_issubset(CAP_FULL_SET, new->cap_effective) ||
new->euid != 0 || new->uid != 0 ||
issecure(SECURE_NOROOT)) {
ret = audit_log_bprm_fcaps(bprm, new, old);
if (ret < 0)
return ret;
}
}
new->securebits &= ~issecure_mask(SECURE_KEEP_CAPS);
return 0;
}
検証サンプル
#include <sys/syscall.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#define _LINUX_CAPABILITY_VERSION_1 0x19980330
#define _LINUX_CAPABILITY_U32S_1 1
typedef unsigned int __u32;
struct cap_header {
__u32 version;
int pid;
};
struct cap_data {
__u32 effective;
__u32 permitted;
__u32 inheritable;
};
void get_cap(char *arg);
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
struct cap_header hdrp;
struct cap_data datap;
int ret = 0;
int pid;
get_cap("original process");
hdrp.pid = 0;
hdrp.version = _LINUX_CAPABILITY_VERSION_1;
datap.effective =1;
datap.permitted =1;
datap.inheritable =1;
if (!syscall(SYS_capset, &hdrp, &datap)) {
get_cap("capsetted process");
sleep(1);
execl("./getcap", "getcap", "exec", (char *) 0);
}
else {
printf("capset err\n");
}
}
void get_cap(char *arg)
{
struct cap_header hdrp;
struct cap_data datap;
int ret = 0;
hdrp.pid = 0;
hdrp.version = _LINUX_CAPABILITY_VERSION_1;
ret = syscall(SYS_capget, &hdrp, &datap);
printf("[%s]\n", arg);
if (!ret) {
printf(" effective :%08x\n", datap.effective);
printf(" permitted :%08x\n", datap.permitted);
printf(" inheritable:%08x\n", datap.inheritable);
}
else {
printf("err:%d\n", ret);
}
}
検証結果・uid=0/ueid!=0のケース
[root@localhost test]# chmod u+s getcap [root@localhost test]# ls -l getcap -rwsr-xr-x 1 kitamura root 5177 9月 20 08:31 getcap
[root@localhost test]# ./a.out [original process] effective :ffffffff permitted :ffffffff inheritable:00000000 [capsetted process] effective :00000001 permitted :00000001 inheritable:00000001 exec effective :00000000:00000000 permitted :ffffffff:ffffffff inheritable:00000000:00000001
・uid=0/ueid=0のケース
[root@localhost test]# chmod u-s getcap [root@localhost test]# ls -l getcap -rwxr-xr-x 1 kitamura root 5177 9月 20 08:31 getcap
[root@localhost test]# ./a.out [original process] effective :ffffffff permitted :ffffffff inheritable:00000000 [capsetted process] effective :00000001 permitted :00000001 inheritable:00000001 exec effective :ffffffff:ffffffff permitted :ffffffff:ffffffff inheritable:00000000:00000001getcapコマンド
#include <sys/syscall.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#define _LINUX_CAPABILITY_VERSION_2 0x20071026
typedef unsigned int __u32;
struct cap_header {
__u32 version;
int pid;
};
struct cap_data {
__u32 effective;
__u32 permitted;
__u32 inheritable;
};
void main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
struct cap_header hdrp;
struct cap_data datap[2];
int i, ret;
if (argc == 2) {
printf("%s\n", argv[1]);
}
hdrp.pid = 0;
hdrp.version = _LINUX_CAPABILITY_VERSION_2;
ret = syscall(SYS_capget, &hdrp, &datap);
if (!ret) {
printf(" effective :%08x:%08x\n", datap[1].effective, datap[0].effective);
printf(" permitted :%08x:%08x\n", datap[1].permitted, datap[0].permitted);
printf(" inheritable:%08x:%08x\n", datap[1].inheritable, datap[0].inheritable);
}
else {
printf("err:%d\n", ret);
}
}