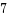mountのリスト
Rev.2を表示中。最新版はこちら。
マウントを管理するためのリストは以下の4つあり、alloc_vfsmnt()の新規のマウントで、struct vfsmountを確保するとき、INIT_LIST_HEADマクロで初期化しています。
struct vfsmount *alloc_vfsmnt(const char *name)
{
struct vfsmount *mnt = kmem_cache_alloc(mnt_cache, GFP_KERNEL);
if (mnt) {
memset(mnt, 0, sizeof(struct vfsmount));
atomic_set(&mnt->mnt_count,1);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&mnt->mnt_hash);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&mnt->mnt_child);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&mnt->mnt_mounts);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&mnt->mnt_list);
if (name) {
int size = strlen(name)+1;
char *newname = kmalloc(size, GFP_KERNEL);
if (newname) {
memcpy(newname, name, size);
mnt->mnt_devname = newname;
}
}
}
return mnt;
}
attach_mnt()で、mnt->mnt_hashは、マウント先のmntとdentryをハッシュキーとする、mount_hashtable[]変数のヘッドへリストされます。パス検索においてdentryがマウントされていると、このリストを辿る事で、すばやくマウント先のmntを取得する事が可能となります。mnt->mnt_listはlist_splice()でcurrent->namespace->listにリストされて、ネームスペース下にマウントされているファイルシステムを管理できます。
mnt->mnt_childはstruct nameidataのmnt->mnt_mountsにリストされます。これはループバックデバイスとかbindマウント等で、既存のmntを複写して、新たにmntを作成する時、このファイルシステムがどれだけ多重に使用されているかの管理かと思います。
static int graft_tree(struct vfsmount *mnt, struct nameidata *nd)
{
int err;
if (mnt->mnt_sb->s_flags & MS_NOUSER)
return -EINVAL;
if (S_ISDIR(nd->dentry->d_inode->i_mode) !=
S_ISDIR(mnt->mnt_root->d_inode->i_mode))
return -ENOTDIR;
err = -ENOENT;
down(&nd->dentry->d_inode->i_sem);
if (IS_DEADDIR(nd->dentry->d_inode))
goto out_unlock;
err = security_sb_check_sb(mnt, nd);
if (err)
goto out_unlock;
err = -ENOENT;
spin_lock(&vfsmount_lock);
if (IS_ROOT(nd->dentry) || !d_unhashed(nd->dentry)) {
struct list_head head;
attach_mnt(mnt, nd);
list_add_tail(&head, &mnt->mnt_list);
list_splice(&head, current->namespace->list.prev);
mntget(mnt);
err = 0;
}
spin_unlock(&vfsmount_lock);
out_unlock:
up(&nd->dentry->d_inode->i_sem);
if (!err)
security_sb_post_addmount(mnt, nd);
return err;
}
static void attach_mnt(struct vfsmount *mnt, struct nameidata *nd)
{
mnt->mnt_parent = mntget(nd->mnt);
mnt->mnt_mountpoint = dget(nd->dentry);
list_add(&mnt->mnt_hash, mount_hashtable+hash(nd->mnt, nd->dentry));
list_add_tail(&mnt->mnt_child, &nd->mnt->mnt_mounts);
nd->dentry->d_mounted++;
}
lookup_mnt()は、パス検索でdentryがマウントされている時、そのマウント先を検索します。これは mount_hashtable[]のhash(mnt, dentry)をキーとし、そのリストを走査することで行っています。
struct vfsmount *lookup_mnt(struct vfsmount *mnt, struct dentry *dentry)
{
struct list_head * head = mount_hashtable + hash(mnt, dentry);
struct list_head * tmp = head;
struct vfsmount *p, *found = NULL;
spin_lock(&vfsmount_lock);
for (;;) {
tmp = tmp->next;
p = NULL;
if (tmp == head)
break;
p = list_entry(tmp, struct vfsmount, mnt_hash);
if (p->mnt_parent == mnt && p->mnt_mountpoint == dentry) {
found = mntget(p);
break;
}
}
spin_unlock(&vfsmount_lock);
return found;
}
umount時、mnt->mnt_child/mnt->mnt_mounts/mnt->mnt_listは、このアンマウントするファイルシステムにぶら下がるファイルシステムもアンマウントする必要があり、従ってその処理のために参照されています。