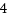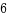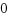hw_breakpoint
Rev.1を表示中。最新版はこちら。
hw_breakpointは、指定したカーネルシンボルを参照した時にトラップを設定します。kprobeは関数コールをトラップするためのブレイクポインで、ブレイクさせる関数の先頭にソフト割り込みに書き換える事で実現していました。hw_breakpointはハードウエアブレイクポイントの略で、CPUのデバッグレジスタにてブレイクポイントを実現しています。下記はカーネルソースにあるサンプルです。指定したコマンド引数のシンボルを参照した時、sample_hbp_handler()がコールされます。引数なしでinsmodすると、カーネルシンボルpid_maxを参照した時トラップします。そしてプロセスIDおよびスタックの情報(コールトレース)を表示させています。
struct perf_event_attr attrに設定するブレイクする条件です。
enum {
HW_BREAKPOINT_LEN_1 = 1,
HW_BREAKPOINT_LEN_2 = 2,
HW_BREAKPOINT_LEN_4 = 4,
HW_BREAKPOINT_LEN_8 = 8,
};
enum {
HW_BREAKPOINT_EMPTY = 0,
HW_BREAKPOINT_R = 1,
HW_BREAKPOINT_W = 2,
HW_BREAKPOINT_RW = HW_BREAKPOINT_R | HW_BREAKPOINT_W,
HW_BREAKPOINT_X = 4,
HW_BREAKPOINT_INVALID = HW_BREAKPOINT_RW | HW_BREAKPOINT_X,
};
#include <linux/module.h> /* Needed by all modules */
#include <linux/kernel.h> /* Needed for KERN_INFO */
#include <linux/init.h> /* Needed for the macros */
#include <linux/kallsyms.h>
#include <linux/perf_event.h>
#include <linux/hw_breakpoint.h>
struct perf_event * __percpu *sample_hbp;
static char ksym_name[KSYM_NAME_LEN] = "pid_max";
module_param_string(ksym, ksym_name, KSYM_NAME_LEN, S_IRUGO);
MODULE_PARM_DESC(ksym, "Kernel symbol to monitor; this module will report any"
" write operations on the kernel symbol");
static void sample_hbp_handler(struct perf_event *bp,
struct perf_sample_data *data,
struct pt_regs *regs)
{
printk(KERN_INFO "%s value is changed\n", ksym_name);
dump_stack();
printk(KERN_INFO "Dump stack from sample_hbp_handler\n");
}
static int __init hw_break_module_init(void)
{
int ret;
struct perf_event_attr attr;
hw_breakpoint_init(&attr);
attr.bp_addr = kallsyms_lookup_name(ksym_name);
attr.bp_len = HW_BREAKPOINT_LEN_4;
attr.bp_type = HW_BREAKPOINT_W | HW_BREAKPOINT_R;
sample_hbp = register_wide_hw_breakpoint(&attr, sample_hbp_handler, NULL);
if (IS_ERR((void __force *)sample_hbp)) {
ret = PTR_ERR((void __force *)sample_hbp);
goto fail;
}
printk(KERN_INFO "HW Breakpoint for %s write installed\n", ksym_name);
return 0;
fail:
printk(KERN_INFO "Breakpoint registration failed\n");
return ret;
}
static void __exit hw_break_module_exit(void)
{
unregister_wide_hw_breakpoint(sample_hbp);
printk(KERN_INFO "HW Breakpoint for %s write uninstalled\n", ksym_name);
}
module_init(hw_break_module_init);
module_exit(hw_break_module_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
MODULE_AUTHOR("K.Prasad");
MODULE_DESCRIPTION("ksym breakpoint");
pid_maxを超えないようにプロセスIDを割り当てるため(たぶん)、新規プロセス作成(sys_clone)時、必ずpid_maxは参照されるはずです。ここでは、bashuからdmesgを起動したということで、comm: bashはbashコマンドがシステムコールのsys_cloneを呼び出し、そこからdo_fork/alloc_pidとコールされ、最後にトラップしたサンプルモジュールのsample_hbp_handler/printkとしてdump_stack()がこのメッセージを表示させている事が分かります。
[46653.374152] pid_max value is changed [46653.374152] Pid: 4391, comm: bash Tainted: G O 3.3.8-1.fc16.i686 #1 [46653.374152] Call Trace: [46653.374152] [<c0926d29>] ? printk+0x2d/0x2f [46653.374152] [<e6f0c000>] ? 0xe6f0bfff [46653.374152] [<e6f0c024>] sample_hbp_handler+0x24/0x34 [break] [46653.374152] [<c04e2a2a>] __perf_event_overflow+0xaa/0x260 [46653.374152] [<c04e2c31>] perf_swevent_overflow+0x51/0x70 [46653.374152] [<c04e2d56>] perf_swevent_event+0x106/0x110 [46653.374152] [<c04e3696>] perf_bp_event+0x76/0x80 [46653.374152] [<c09306bf>] hw_breakpoint_exceptions_notify+0xff/0x120 [46653.374152] [<c09322d5>] notifier_call_chain+0x45/0x60 [46653.374152] [<c0932342>] atomic_notifier_call_chain+0x22/0x30 [46653.374152] [<c093237d>] notify_die+0x2d/0x30 [46653.374152] [<c092fb7a>] do_debug+0x8a/0x180 [46653.374152] [<c092f668>] debug_stack_correct+0x30/0x38 [46653.374152] [<c0451c4e>] ? alloc_pid+0x1e/0x380 [46653.374152] [<c0451c88>] ? alloc_pid+0x58/0x380 [46653.374152] [<c0435cdd>] copy_process+0xb4d/0x10a0 [46653.374152] [<c0436364>] do_fork+0xf4/0x340 [46653.374152] [<c0532a3c>] ? fd_install+0x2c/0x60 [46653.374152] [<c040ae94>] sys_clone+0x34/0x40 [46653.374152] [<c09359d9>] ptregs_clone+0x15/0x3c [46653.374152] [<c093589f>] ? sysenter_do_call+0x12/0x28 [46653.374152] Dump stack from sample_hbp_handlerdump_stack()は以下のように実装されています。tainted: Gはシステムとして問題ない。と言うことで、?はアドレスの内容に信頼性ないと言うことです。
void dump_stack(void)
{
unsigned long bp;
unsigned long stack;
bp = stack_frame(current, NULL);
printk("Pid: %d, comm: %.20s %s %s %.*s\n",
current->pid, current->comm, print_tainted(),
init_utsname()->release,
(int)strcspn(init_utsname()->version, " "),
init_utsname()->version);
show_trace(NULL, NULL, &stack, bp);
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(dump_stack);
static const struct tnt tnts[] = {
{ TAINT_PROPRIETARY_MODULE, 'P', 'G' },
{ TAINT_FORCED_MODULE, 'F', ' ' },
{ TAINT_UNSAFE_SMP, 'S', ' ' },
{ TAINT_FORCED_RMMOD, 'R', ' ' },
{ TAINT_MACHINE_CHECK, 'M', ' ' },
{ TAINT_BAD_PAGE, 'B', ' ' },
{ TAINT_USER, 'U', ' ' },
{ TAINT_DIE, 'D', ' ' },
{ TAINT_OVERRIDDEN_ACPI_TABLE, 'A', ' ' },
{ TAINT_WARN, 'W', ' ' },
{ TAINT_CRAP, 'C', ' ' },
{ TAINT_FIRMWARE_WORKAROUND, 'I', ' ' },
{ TAINT_OOT_MODULE, 'O', ' ' },
};
const char *print_tainted(void)
{
static char buf[ARRAY_SIZE(tnts) + sizeof("Tainted: ") + 1];
if (tainted_mask) {
char *s;
int i;
s = buf + sprintf(buf, "Tainted: ");
for (i = 0; i < ARRAY_SIZE(tnts); i++) {
const struct tnt *t = &tnts[i];
*s++ = test_bit(t->bit, &tainted_mask) ?
t->true : t->false;
}
*s = 0;
} else
snprintf(buf, sizeof(buf), "Not tainted");
return buf;
}