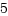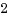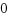execのpid/tid/sid/pgid
Rev.1を表示中。最新版はこちら。
execでコマンドを実行すると、実行元タスクがスレッドなら、プロセスID等は実行元タスクのグループリーダ(通常は親プロセス)のプロセスID等に更新されます。検証サンプル
#define _GNU_SOURCE
#include <sched.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/syscall.h>
#include <unistd.h>
void get_pid(char *);
static int childFunc(void *arg)
{
get_pid("clone");
execl("./show_pid", "./exe_pid", NULL);
eturn 0;
}
#define STACK_SIZE (1024 * 1024)
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
char *stack;
char *stackTop;
pid_t pid;
stack = malloc(STACK_SIZE);
stackTop = stack + STACK_SIZE;
if(argc == 2) {
get_pid("thread parent");
pid = clone(childFunc, stackTop, CLONE_THREAD | CLONE_SIGHAND | CLONE_VM, NULL);
}
else {
get_pid("parent");
pid = clone(childFunc, stackTop, 0, NULL);
}
sleep(1);
waitpid(pid, NULL, 0);
exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
}
void get_pid(char* p)
{
printf("%-20s: pid=%d, tid=%d, sid=%d gid=%d\n",
p,
syscall(SYS_getpid),
syscall(SYS_gettid),
syscall(SYS_getsid, 0),
syscall(SYS_getpgid, 0));
}
show_pid.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/syscall.h>
void main()
{
printf("%-20s: pid=%d, tid=%d, sid=%d gid=%d\n",
"exe cmd",
syscall(SYS_getpid),
syscall(SYS_gettid),
syscall(SYS_getsid, 0),
syscall(SYS_getpgid, 0));
}
結果
スレッドグループリーダのプロセス(pid=tid)なら、cloneプロセスのidとなり、cloneタスクと差し替えます。[root@localhost test]# ./a.out parent : pid=12069, tid=12069, sid=11772 gid=12069 clone : pid=12070, tid=12070, sid=11772 gid=12069 exe cmd : pid=12070, tid=12070, sid=11772 gid=12069スレッド(pid != tid)なら、スレッドの親プロセスのidとなり、thread parentと差し替えます。(呼び出し元スレッドのcloneはkillされます。)
[root@localhost test]# ./a.out thread thread parent : pid=12072, tid=12072, sid=11772 gid=12072 clone : pid=12072, tid=12073, sid=11772 gid=12072 exe cmd : pid=12072, tid=12072, sid=11772 gid=12072execlは、struct linux_binfmtの.load_shlibコールバックからflush_old_exec()がコールされ、該当するタスクと差し替えます。その時、de_thread()で差替えられるプロセスの処理と、差替えるプロセスのIDが設定されます。
static struct linux_binfmt elf_format = {
.module = THIS_MODULE,
.load_binary = load_elf_binary,
.load_shlib = load_elf_library,
.core_dump = elf_core_dump,
.min_coredump = ELF_EXEC_PAGESIZE,
};
tskは差替えられるタスクです。thread_group_empty(tsk)は子スレッドを有しているかチェックします。子スレッド有しているなら、そのスレッド削除します。子のプロセスは親とリソースは独立しているため問題ありません。子プロセスのスレッド有無のチェックは、thread_group_empty(tsk)で行います。tskがスレッドでもthread_group_empty(tsk)はFALSEとなります。従ってgoto no_thread_groupはスレッドを有しないプロセスのみです。
存在する子スレッドを削除し、if (!thread_group_leader(tsk))で、tskがスレッドの場合の処理となります。
スレッドの場合、leader = tsk->group_leaderは親プロセスです。tsk->group_leader = tskでexecはスレッドグループリーダとなり、親プロセスIDをexecのtskのPIDTYPE_PIDとし、親プロセスのpid/tidと同値となり、transfer_pid()は、スレッドリストのヘッドのleaderをtskに差し替えることで、スレッドのtask_structがスレッドグループリーダとなります。
親だったプロセスは、exeのスレッドと名実ともに入れ替わり、leader->exit_state = EXIT_DEAD/release_task(leader)で親のリソースは解放されます。
static int de_thread(struct task_struct *tsk)
{
struct signal_struct *sig = tsk->signal;
struct sighand_struct *oldsighand = tsk->sighand;
spinlock_t *lock = &oldsighand->siglock;
if (thread_group_empty(tsk))
goto no_thread_group;
spin_lock_irq(lock);
if (signal_group_exit(sig)) {
spin_unlock_irq(lock);
return -EAGAIN;
}
sig->group_exit_task = tsk;
sig->notify_count = zap_other_threads(tsk);
if (!thread_group_leader(tsk))
sig->notify_count--;
while (sig->notify_count) {
__set_current_state(TASK_UNINTERRUPTIBLE);
spin_unlock_irq(lock);
schedule();
spin_lock_irq(lock);
}
spin_unlock_irq(lock);
if (!thread_group_leader(tsk)) {
struct task_struct *leader = tsk->group_leader;
sig->notify_count = -1; /* for exit_notify() */
for (;;) {
write_lock_irq(&tasklist_lock);
if (likely(leader->exit_state))
break;
__set_current_state(TASK_UNINTERRUPTIBLE);
write_unlock_irq(&tasklist_lock);
schedule();
}
tsk->start_time = leader->start_time;
BUG_ON(!same_thread_group(leader, tsk));
BUG_ON(has_group_leader_pid(tsk));
detach_pid(tsk, PIDTYPE_PID);
tsk->pid = leader->pid;
attach_pid(tsk, PIDTYPE_PID, task_pid(leader));
transfer_pid(leader, tsk, PIDTYPE_PGID);
transfer_pid(leader, tsk, PIDTYPE_SID);
list_replace_rcu(&leader->tasks, &tsk->tasks);
list_replace_init(&leader->sibling, &tsk->sibling);
tsk->group_leader = tsk;
leader->group_leader = tsk;
tsk->exit_signal = SIGCHLD;
leader->exit_signal = -1;
BUG_ON(leader->exit_state != EXIT_ZOMBIE);
leader->exit_state = EXIT_DEAD;
if (unlikely(leader->ptrace))
__wake_up_parent(leader, leader->parent);
write_unlock_irq(&tasklist_lock);
release_task(leader);
}
sig->group_exit_task = NULL;
sig->notify_count = 0;
no_thread_group:
tsk->exit_signal = SIGCHLD;
if (current->mm)
setmax_mm_hiwater_rss(&sig->maxrss, current->mm);
exit_itimers(sig);
flush_itimer_signals();
if (atomic_read(&oldsighand->count) != 1) {
struct sighand_struct *newsighand;
newsighand = kmem_cache_alloc(sighand_cachep, GFP_KERNEL);
if (!newsighand)
return -ENOMEM;
atomic_set(&newsighand->count, 1);
memcpy(newsighand->action, oldsighand->action,
sizeof(newsighand->action));
write_lock_irq(&tasklist_lock);
spin_lock(&oldsighand->siglock);
rcu_assign_pointer(tsk->sighand, newsighand);
spin_unlock(&oldsighand->siglock);
write_unlock_irq(&tasklist_lock);
__cleanup_sighand(oldsighand);
}
BUG_ON(!thread_group_leader(tsk));
return 0;
}
copy_process()で、スレッドはグループリーダの親のthread_groupをヘッダーとするリストに必ず登録され、初期値であるlist->next = listは、スレッドならlist->next != listです。従ってthread_group_empty()はFALSEとなります。
copy_process()
{
:
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&p->thread_group);
:
if (clone_flags & CLONE_THREAD) {
current->signal->nr_threads++;
atomic_inc(¤t->signal->live);
atomic_inc(¤t->signal->sigcnt);
p->group_leader = current->group_leader;
list_add_tail_rcu(&p->thread_group, &p->group_leader->thread_group);
}
:
}
static inline void INIT_LIST_HEAD(struct list_head *list)
{
list->next = list;
list->prev = list;
}
static inline int thread_group_empty(struct task_struct *p)
{
return list_empty(&p->thread_group);
}
static inline int list_empty(const struct list_head *head)
{
return head->next == head;
}