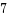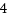O_CLOEXEC
Rev.6を表示中。最新版はこちら。
[root@localhost v.north]# cat cloexec1.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <ctype.h>
void exe(int fdindex);
void main(int argc,char **argv)
{
int fd;
char cmd[32];
if (!strcmp(argv[1], "O_CLOEXEC")) {
fd =open("babakaka.txt", O_RDWR | O_CLOEXEC);
}
else {
fd =open("babakaka.txt", O_RDWR);
}
sprintf(cmd, "./cloexec2 system %d", fd);
system(cmd);
exe(fd);
}
void exe(int fdindex)
{
char fd[8];
sprintf(fd, "%d", fdindex);
execl("./cloexec2", "./cloexec2", "exe", fd, NULL);
}
[root@localhost v.north]# cat cloexec2.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <string.h>
void main(int argc,char *argv[])
{
int fd = atoi(argv[2]);
char buff[32];
int cnt;
printf("%-10s:", argv[1]);
memset(buff, 0, 32);
cnt = read(fd, buff, 8);
if (cnt >=0 ) {
printf("child:%s\n", buff);
}
else {
printf("child:no read\n");
}
}
[root@localhost v.north]# cat babakaka.txt aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa [root@localhost v.north]# ./cloexec1 O_CLOEXEC system :child:no read exe :child:no read [root@localhost v.north]# ./cloexec1 O_NOCLOEXEC system :child:aaaaaaaa exe :child:aaaaaaaa
forkは親プロセスのcurrent->filesを継承します。systemはforkしたプロセスでexeがコールされ、O-CLOEXECはビット単位でのインデックスで、close_on_exec_init[1]による設定で、exeシステムコールで係るインデックスのファイルは継承されません。
current->files->close_on_exec_init[1]
current->files->fd_array[fdindex]
プロセス間でのファイル参照はプロセス間でファイルオープンすればよく、O_NOCLOEXECはpipeの運用上の実装かと。で係る説明はpipeでの説明が多々見受けられますが、実装的にはexeシステムコールでの実装で、故にpipe以外の全ファイルに適用されます。
static inline void __set_close_on_exec(int fd, struct fdtable *fdt)
{
__set_bit(fd, fdt->close_on_exec);
}
static inline void __clear_close_on_exec(int fd, struct fdtable *fdt)
{
__clear_bit(fd, fdt->close_on_exec);
}