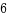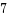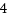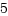O_CLOEXEC
Rev.3を表示中。最新版はこちら。
ファイルモードがO_CLOEXECなら、exec(外部コマンド)によるプロセスでは、そのファイルを参照する事はできません。
[root@localhost c]# cat closeexec1.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
void main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
int pfd1[2], pfd2[2];
pipe2(pfd1, 0);
dup3(pfd1[0], 253, 0);
pipe2(pfd2, 0);
dup3(pfd2[0], 254, O_CLOEXEC);
write(pfd1[1], "01234", 5);
write(pfd2[1], "56789", 5);
system("./closeexec2.o");
}
[root@localhost c]# cat closeexec2.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
void main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
int ret;
char buff[6];
printf("read from NO_O_CLOEXEC\n");
memset(buff, 0, 6);
ret = read(253,buff, 5);
printf("%2d:%s\n", ret, buff);
printf("read from O_CLOEXEC\n");
memset(buff, 0, 6);
ret = read(254,buff, 5);
printf("%2d:%s\n", ret, buff);
}
[root@localhost c]# ./closeexec1.o read from NO_O_CLOEXEC 5:01234 read from O_CLOEXEC -1:alloc_fd()でcurrent->file[file ID] = struct file *file;としファイルIDを取得します。flagsがO_CLOEXECなら、そのファイルIDをcurrent->files->fdt->close_on_execのビット位置として設定され、forkで継承した子プロセスのclose_on_execのビット位置の掛かるファイルをexecでcloseされます。
#define FD_SET(fd,fdsetp) __FD_SET(fd,fdsetp)
int alloc_fd(unsigned start, unsigned flags)
{
struct files_struct *files = current->files;
unsigned int fd;
int error;
struct fdtable *fdt;
spin_lock(&files->file_lock);
repeat:
fdt = files_fdtable(files);
fd = start;
if (fd < files->next_fd)
fd = files->next_fd;
if (fd < fdt->max_fds)
fd = find_next_zero_bit(fdt->open_fds->fds_bits,
fdt->max_fds, fd);
error = expand_files(files, fd);
if (error < 0)
goto out;
if (error)
goto repeat;
if (start <= files->next_fd)
files->next_fd = fd + 1;
FD_SET(fd, fdt->open_fds);
if (flags & O_CLOEXEC)
FD_SET(fd, fdt->close_on_exec);
else
FD_CLR(fd, fdt->close_on_exec);
error = fd;
#if 1
if (rcu_dereference_raw(fdt->fd[fd]) != NULL) {
printk(KERN_WARNING "alloc_fd: slot %d not NULL!\n", fd);
rcu_assign_pointer(fdt->fd[fd], NULL);
}
#endif
out:
spin_unlock(&files->file_lock);
return error;
}
O_CLOEXECできるファイルIDの最大は1024で、longサイズが4バイト時fds_bits[32]です。
#define __NFDBITS (8 * sizeof(unsigned long))
#define __FD_SETSIZE 1024
#define __FDSET_LONGS (__FD_SETSIZE/__NFDBITS)
typedef struct {
unsigned long fds_bits [__FDSET_LONGS];
} __kernel_fd_set;
static inline void __FD_SET(unsigned long __fd, __kernel_fd_set *__fdsetp)
{
unsigned long __tmp = __fd / __NFDBITS;
unsigned long __rem = __fd % __NFDBITS;
__fdsetp->fds_bits[__tmp] |= (1UL<<__rem);
}
execはsearch_binary_handler()でコマンドファイルのファイルシステムのstruct linux_binfmtを取得し、load_elf_binaryコールバックでコマンドイメージをロードします。この時、flush_old_files()でfdt->close_on_exec->fds_bits[]毎のセットされているビット位置をファイルIDとするファイルをクローズします。
static void flush_old_files(struct files_struct * files)
{
long j = -1;
struct fdtable *fdt;
spin_lock(&files->file_lock);
for (;;) {
unsigned long set, i;
j++;
i = j * __NFDBITS;
fdt = files_fdtable(files);
if (i >= fdt->max_fds)
break;
set = fdt->close_on_exec->fds_bits[j];
if (!set)
continue;
fdt->close_on_exec->fds_bits[j] = 0;
spin_unlock(&files->file_lock);
for ( ; set ; i++,set >>= 1) {
if (set & 1) {
sys_close(i);
}
}
spin_lock(&files->file_lock);
}
spin_unlock(&files->file_lock);
}