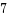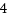O_CLOEXEC
Rev.1を表示中。最新版はこちら。
O_CLOEXECでない場合、fork_childはparentのファイルIDでファイル参照でき、新規オープンしたファイルIDは3となりますが、O_CLOEXECの時、parentのファイルIDでファイル参照できません。(実際はエラーとなります。)そして新規オープンしたファイルIDは2となっています。ファイルIDの0/1/2は標準入力/標準出力/標準エラです。
[root@localhost lkm]# cat parent.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <string.h>
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
int fd;
char fileID[4];
char buff[10];
if (argc == 1) {
fd = open("hoge1", O_RDWR);
}
else {
fd = open("hoge1", O_CLOEXEC|O_RDWR);
}
sprintf(fileID, "%d", fd);
printf("--parent--\n");
memset(buff, 0, 10);
read(fd, buff, 5);
printf("%d:%s\n", fd, buff);
if (!fork()) {
execlp("./fork_child", "./fork_child", fileID, NULL);
}
sleep(1);
printf("--parent--\n");
memset(buff, 0, 10);
read(fd, buff, 5);
printf("%d:%s\n", fd, buff);
close(fd);
}
[root@localhost lkm]# cat fork_child.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <string.h>
void main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
char buff[10];
printf("---child---\n");
memset(buff, 0, sizeof(buff));
read(atoi(argv[1]), buff, 5);
printf("%d:%s\n", atoi(argv[1]), buff);
int fd = open("hoge2", O_RDWR);
printf("new fileID:%d\n", fd);
}
実行結果
[root@localhost kitamura]# echo 0123456789abcde > hoge1 [root@localhost kitamura]# ./parent --parent-- 3:01234 ---child--- 3:56789 new fileID:4 --parent-- 3:abcde [root@localhost kitamura]# ./parent O_CLOEXEC --parent-- 3:01234 ---child--- 3: new fileID:3 --parent-- 3:56789forkは親プロセスのメモリ空間を共有(メモリの書き込みはCOWにて動的に割り当てられます。)し、プロセスstructの属性も、copy_process()で親プロセスの属性を共有します。ファイルIDについては、 copy_files()がコールされます。
親プロセスのcurrent->filesからdup_fd()で共有したstruct files_struct newfを取得し、それを新規プロセスのtsk->filesといたします。
static int copy_files(unsigned long clone_flags, struct task_struct *tsk)
{
struct files_struct *oldf, *newf;
int error = 0;
oldf = current->files;
if (!oldf)
goto out;
if (clone_flags & CLONE_FILES) {
atomic_inc(&oldf->count);
goto out;
}
newf = dup_fd(oldf, &error);
if (!newf)
goto out;
tsk->files = newf;
error = 0;
out:
return error;
}
execは実行するfileのセグメントから、binfmtを取得し、struct linux_binfmtの掛かるローダの.load_binaryコールバックでロードされます。elfはload_elf_binary()がコールされ、そこでsetup_new_exec()/flush_old_files()をコールし、fdt->close_on_exec->fds_bits[]のセットしているビットに応じて、そのファイルをcloseします。O_CLOEXECでオープンされたファイルはそのビットがセットされます。従ってfds_bits[]がセットされていないO_CLOEXECでないファイルIDは、オープン状態となります。
static struct linux_binfmt elf_format = {
.module = THIS_MODULE,
.load_binary = load_elf_binary,
.load_shlib = load_elf_library,
.core_dump = elf_core_dump,
.min_coredump = ELF_EXEC_PAGESIZE,
};
void setup_new_exec(struct linux_binprm * bprm)
{
arch_pick_mmap_layout(current->mm);
current->sas_ss_sp = current->sas_ss_size = 0;
if (current_euid() == current_uid() && current_egid() == current_gid())
set_dumpable(current->mm, 1);
else
set_dumpable(current->mm, suid_dumpable);
set_task_comm(current, bprm->tcomm);
current->mm->task_size = TASK_SIZE;
if (bprm->cred->uid != current_euid() ||
bprm->cred->gid != current_egid()) {
current->pdeath_signal = 0;
} else {
would_dump(bprm, bprm->file);
if (bprm->interp_flags & BINPRM_FLAGS_ENFORCE_NONDUMP)
set_dumpable(current->mm, suid_dumpable);
}
if (!get_dumpable(current->mm))
perf_event_exit_task(current);
current->self_exec_id++;
flush_signal_handlers(current, 0);
flush_old_files(current->files);
}
static void flush_old_files(struct files_struct * files)
{
long j = -1;
struct fdtable *fdt;
spin_lock(&files->file_lock);
for (;;) {
unsigned long set, i;
j++;
i = j * __NFDBITS;
fdt = files_fdtable(files);
if (i >= fdt->max_fds)
break;
set = fdt->close_on_exec->fds_bits[j];
if (!set)
continue;
fdt->close_on_exec->fds_bits[j] = 0;
spin_unlock(&files->file_lock);
for ( ; set ; i++,set >>= 1) {
if (set & 1) {
sys_close(i);
}
}
spin_lock(&files->file_lock);
}
spin_unlock(&files->file_lock);
}