Boundary Buffer
Rev.5を表示中。最新版はこちら。
概要
BufferのフラグBH_Boundaryに関して。
BH_Boundary 意味
カーネルのfs/mpage.cにBH_Boundaryに関してコメントがあるので、その抜粋と注釈。
==== コメントここから ====
BH_Boundary explanation:
There is a problem. The mpage read code assembles several pages, gets all their disk mappings, and then submits them all. That's fine, but obtaining the disk mappings may require I/O. Reads of indirect blocks, for example.
mpageのRead処理は幾つかのページをまとめて処理する際、これらのページ全てのディスクマッピング(*1)を取得します。それからページのI/Oを開始します。これはよくできていますが、ディスクマッピングを取得する場合はI/Oが必要になるかもしれません。例えば、間接参照ブロック(*2)のReadです。
So an mpage read of the first 16 blocks of an ext2 file will cause I/O to be submitted in the following order:
だから、ext2上のファイルの最初の16ブロックのReadは以下の順番でI/Oが発生します。
12 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 13 14 15 16 (*3)
because the indirect block has to be read to get the mappings of blocks 13,14,15,16. Obviously, this impacts performance.
なぜなら13,14,15,16ブロックのマッピングを取得するために間接参照ブロック(*4)を読まなければならないためです。これは、明らかに性能に影響します。
So what we do it to allow the filesystem's get_block() function to set BH_Boundary when it maps block 11. BH_Boundary says: mapping of the block after this one will require I/O against a block which is probably close to this one. So you should push what I/O you have currently accumulated.
ファイルシステムがブロック11をマッピングする際、get_block()にBH_Boundaryを設定させるようにしました。 BH_Boundaryは「このあとのブロックのマッピングで、おそらく、このブロックに近いブロックに対してI/Oが必要になる。だから、今溜めているI/Oを発行すべき。」ということを意味します(*4)。
This all causes the disk requests to be issued in the correct order.
これにより、正しい順番でI/Oを行えるようになります。
==== コメントここまで ====There is a problem. The mpage read code assembles several pages, gets all their disk mappings, and then submits them all. That's fine, but obtaining the disk mappings may require I/O. Reads of indirect blocks, for example.
mpageのRead処理は幾つかのページをまとめて処理する際、これらのページ全てのディスクマッピング(*1)を取得します。それからページのI/Oを開始します。これはよくできていますが、ディスクマッピングを取得する場合はI/Oが必要になるかもしれません。例えば、間接参照ブロック(*2)のReadです。
So an mpage read of the first 16 blocks of an ext2 file will cause I/O to be submitted in the following order:
だから、ext2上のファイルの最初の16ブロックのReadは以下の順番でI/Oが発生します。
12 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 13 14 15 16 (*3)
because the indirect block has to be read to get the mappings of blocks 13,14,15,16. Obviously, this impacts performance.
なぜなら13,14,15,16ブロックのマッピングを取得するために間接参照ブロック(*4)を読まなければならないためです。これは、明らかに性能に影響します。
So what we do it to allow the filesystem's get_block() function to set BH_Boundary when it maps block 11. BH_Boundary says: mapping of the block after this one will require I/O against a block which is probably close to this one. So you should push what I/O you have currently accumulated.
ファイルシステムがブロック11をマッピングする際、get_block()にBH_Boundaryを設定させるようにしました。 BH_Boundaryは「このあとのブロックのマッピングで、おそらく、このブロックに近いブロックに対してI/Oが必要になる。だから、今溜めているI/Oを発行すべき。」ということを意味します(*4)。
This all causes the disk requests to be issued in the correct order.
これにより、正しい順番でI/Oを行えるようになります。
(*1) ページがディスク上のどのブロックに対応しているか。
(*2) ext2ではファイル先頭から12ブロック以降のデータは間接参照となる。
(*3) 想定されているブロックの配置は図1のとおり。ファイルがきれいに連続ブロックに配置されているケース。間接参照となる#12〜の前には間接参照用のポインタ群を格納したブロックが配置されている。
(*4) 図1のBlock offset 12(灰色)のブロック
(*5) mpageでI/Oを発行するルーチンdo_mpage_readpage()ではBufferがBoundaryであったらI/Oをただちにsubmitするようになっている。
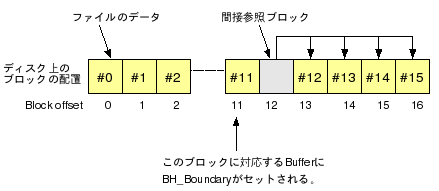
図1 ディスク上のブロック配置例
関連関数
buffer_boundary(bh)
指定バッファがBoundary(BH_Boundaryが立っている)かチェックする。
関連ページ
BufferExt2 FS
mpage
